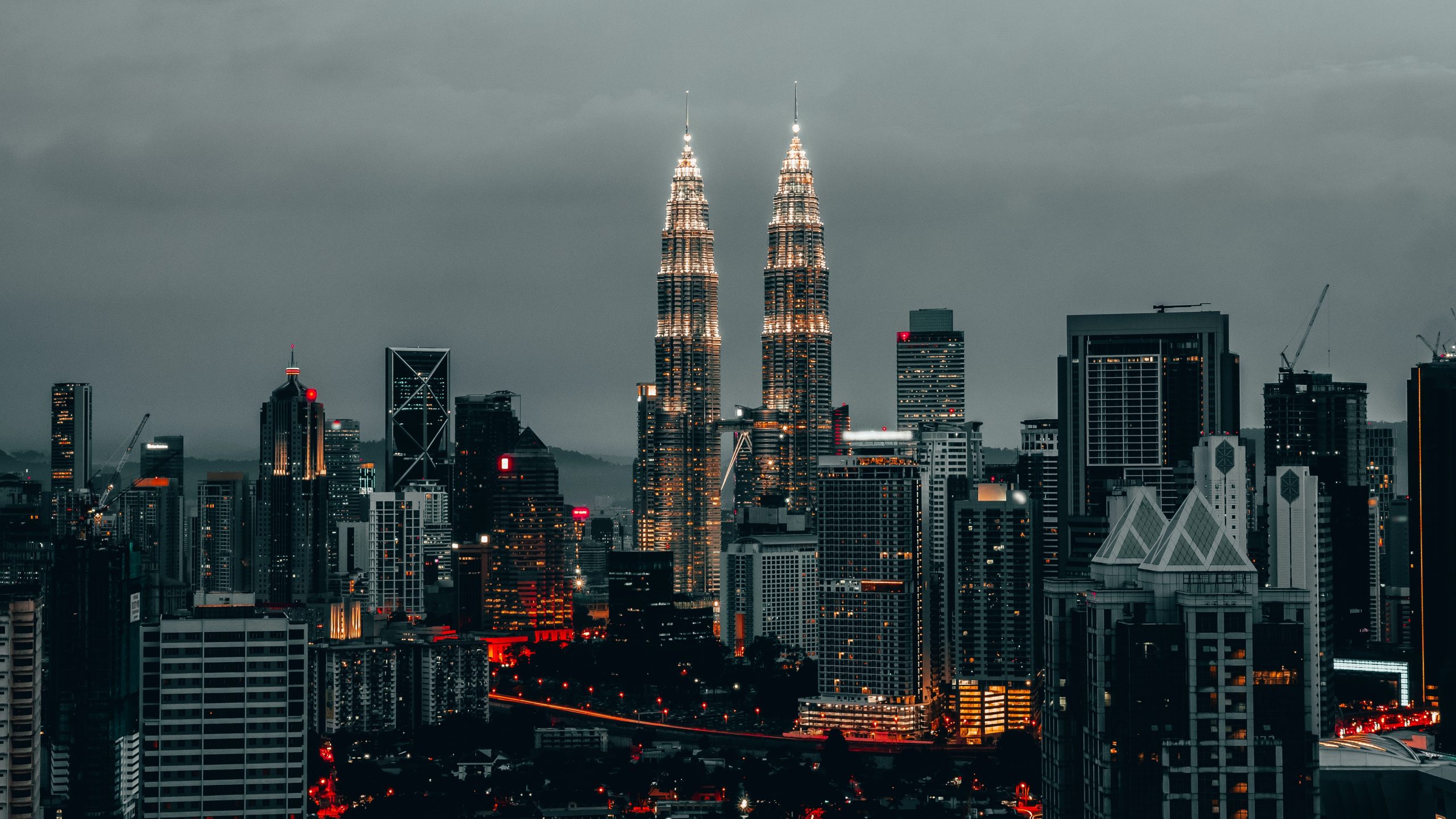
Welcome to Malaysia, a captivating Southeast Asian nation that blends rich cultural diversity, stunning landscapes, and a harmonious fusion of modernity and tradition. Here’s a snapshot of what awaits you:
Malaysia is a real cultural Kaleidoscope where a mix of cultures are living side-by-side, home to Malays, Chinese, Indians, and indigenous groups. This diversity is reflected in its festivals, languages, religions, and of course, its cuisine. Explore bustling markets, vibrant temples, ornate mosques, and colonial-era architecture that paint a vivid picture of the country’s past and present.
From lush rainforests to pristine beaches and towering mountains, Malaysia’s natural beauty is simply awe-inspiring. Discover the dense jungles of Borneo, where orangutans swing through treetops, and trek to the top of Mount Kinabalu for panoramic vistas. On the peninsula, relax on white-sand beaches, explore idyllic islands, or venture into the lush Cameron Highlands for tea plantations and cooler climes.
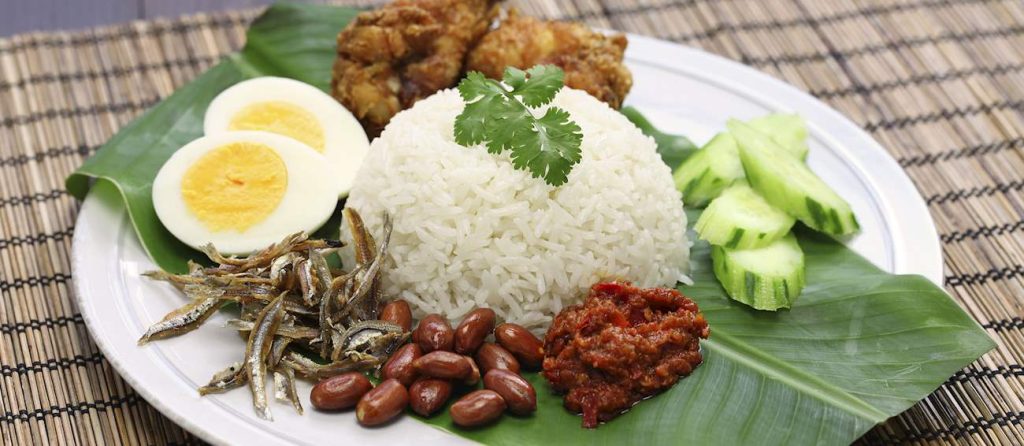
Prepare your taste buds for a culinary journey like no other. Malaysian food is a delightful fusion of flavors, influenced by the country’s diverse cultures. Savor mouthwatering dishes like Nasi Lemak (coconut rice), Roti Canai (flaky bread), Char Kway Teow (stir-fried noodles), and a tantalizing array of street food that promises to excite and satisfy.

In bustling cities like Kuala Lumpur, futuristic skyscrapers stand alongside historic districts, creating a dynamic contrast. Gaze up at the iconic Petronas Twin Towers, shop in high-end malls, and explore the vibrant nightlife. For a glimpse into Malaysia’s past, wander through UNESCO-listed George Town in Penang, with its charming architecture and vibrant street art.
Adventurers will find plenty to keep their hearts racing. Dive into the crystal-clear waters off Sipadan Island to witness stunning marine life, or go caving in Mulu National Park’s intricate underground networks. Wildlife enthusiasts can spot elephants, tigers, and a multitude of bird species in the country’s protected reserves.

Malaysia is known for its warm and welcoming people, whose friendliness will make you feel right at home. Engage with locals, learn about their customs, and take part in cultural experiences to gain a deeper understanding of the country’s traditions.
Indulge in shopping, from bustling markets to high-end malls. Hunt for traditional crafts like batik textiles and intricate pewter items, or find modern fashion and electronics. Malaysia offers a diverse range of items to suit every taste and budget.
Whether you’re drawn to its cultural tapestry, natural wonders, or gastronomic delights, Malaysia promises an unforgettable experience that will leave you enchanted and eager for more. So, pack your bags and prepare to immerse yourself in the captivating beauty of this vibrant nation!
Visa and Residency
Please keep in mind that these requirements can change and vary based on the specific program guidelines, so it’s important to visit the official government website or contact the relevant authorities for the most accurate and up-to-date information. It’s also recommended to consult with immigration professionals who specialize in Malaysia to ensure a smooth application process.
Since circumstances can change, it’s important to double-check the current requirements before making any decisions or plans – as such the below is simply a guide.
- Financial Requirements: Applicants need to demonstrate a certain level of financial capability to support themselves in Malaysia without seeking employment. The specific financial requirements can vary based on factors such as age and location of application. This may involve showing proof of liquid assets, monthly income, and other financial instruments.
- Medical Insurance: Applicants are generally required to have medical insurance coverage from an insurance company that operates in Malaysia.
- Minimum Age: There is typically a minimum age requirement for applicants, usually around 50 years old.
- Security Deposit: Some applicants may need to place a security deposit in a Malaysian bank.
- Health Check: Applicants might need to undergo a medical examination to ensure they’re in good health.
- Income Requirement: Some versions of the program require applicants to meet a specific income requirement.
- Background Checks: Applicants should have a clean criminal record and be of good character.
- Renewal: The initial visa granted through the MM2H program is usually for a period of ten years and is renewable.
Healthcare
Public healthcare in Malaysia is provided by the government and is generally subsidized, making it more affordable for the population. Public hospitals and clinics offer a wide range of medical services, including primary care, specialist consultations, surgeries, and emergency care. Services are often provided at a lower cost compared to private facilities.
However, public healthcare facilities can sometimes experience longer waiting times due to the high demand, and the quality of care might vary depending on the specific location and facility.
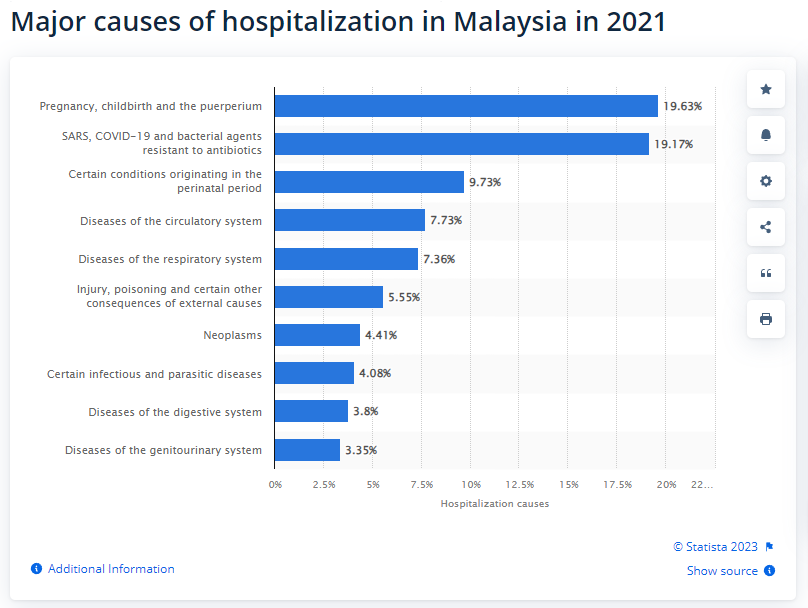
Private healthcare in Malaysia is known for its high-quality services and modern facilities. Private hospitals and clinics offer a wide range of medical treatments and services, often with shorter waiting times compared to public facilities. Many private healthcare facilities cater to expatriates and tourists as well.
While private healthcare can offer a more comfortable and efficient experience, it generally comes at a higher cost compared to public healthcare.
Many Malaysians and expatriates opt for health insurance to cover medical expenses, especially when seeking care in private healthcare facilities. Health insurance helps mitigate the financial burden of medical treatments and consultations.
Medical tourism in Malaysia has gained popularity as a medical tourism destination due to its modern medical facilities, skilled healthcare professionals, and competitive pricing. Many people from neighboring countries and even further abroad travel to Malaysia for medical procedures and treatments.
Pharmacies are widely available throughout Malaysia, offering both prescription and over-the-counter medications. Pharmacists can provide advice on medication and general health concerns.
The Malaysian government has taken steps to improve healthcare accessibility and quality across the country. Initiatives include upgrading healthcare facilities, enhancing medical education, and promoting medical tourism.
Cost of Living
Housing: Housing costs can vary widely based on location, type of accommodation, and whether you choose to live in urban or rural areas. Kuala Lumpur, the capital city, tends to have higher housing costs compared to smaller cities and towns. Rent for a one-bedroom apartment in the city center could range from around RM 1,500 to RM 3,000 per month or even higher.
Food: Malaysia is known for its diverse and affordable food options. You can find street food stalls and local restaurants offering delicious meals at relatively low prices. A basic meal at a local eatery might cost around RM 10 to RM 20, while dining in mid-range restaurants could cost between RM 30 to RM 100 per person.

Transportation: Public transportation in Malaysia is generally affordable. Cities like Kuala Lumpur have an extensive network of buses, trains, and light rail systems. Monthly transportation costs might range from RM 100 to RM 300, depending on usage and location.
Utilities: Monthly utility bills (electricity, water, gas) for a standard apartment could range from RM 150 to RM 300 or more, depending on consumption.
Healthcare: Healthcare costs can vary depending on whether you opt for public or private healthcare services. Basic medical consultations in public hospitals can be affordable, while private healthcare services might be more expensive. Having health insurance is advisable to cover potential medical expenses.
Entertainment and Leisure: Costs for entertainment, movies, dining out, and leisure activities can vary. Malaysia offers a mix of affordable and upscale options to suit different budgets.
Education: If you’re considering education for children, international schools and private institutions might have varying tuition fees. Costs can be significant and will depend on the specific school.
Miscellaneous Expenses: Other expenses such as clothing, personal care, and household items can vary based on individual preferences and lifestyle.
Currency and Economic Considerations
Currency: The currency of Malaysia is the Malaysian Ringgit (MYR), often denoted as RM. The Ringgit is further divided into 100 smaller units called sen. The currency is issued and regulated by the Central Bank of Malaysia, also known as Bank Negara Malaysia.
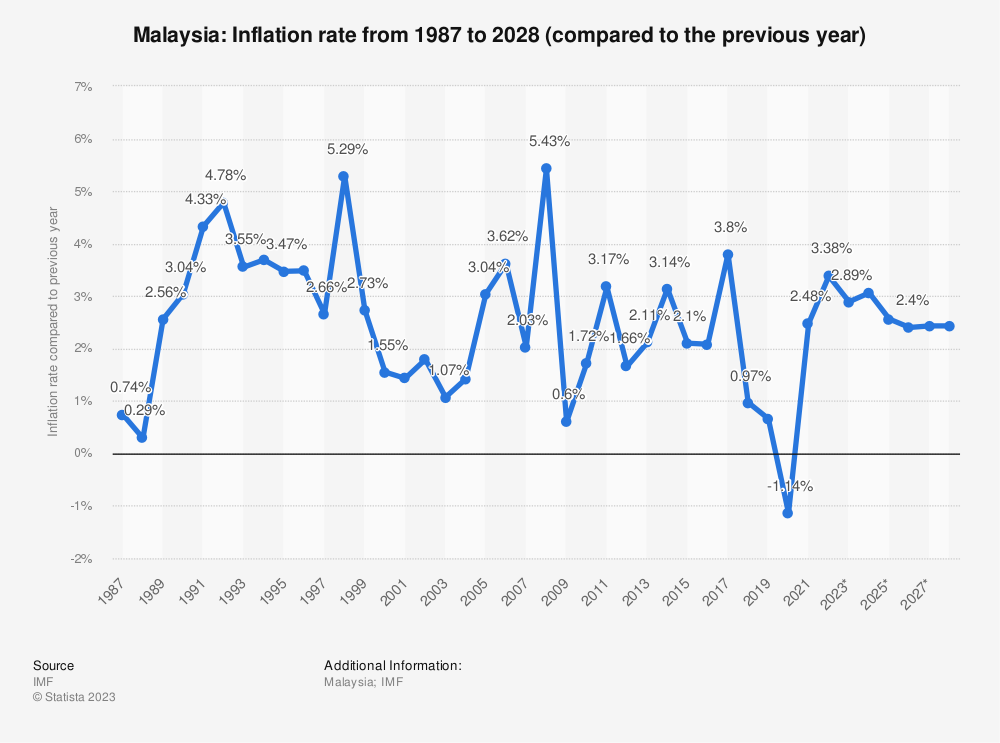
General Inflation Trends: Inflation in Malaysia has historically been relatively moderate. However, inflation rates can fluctuate due to various factors such as changes in global oil prices, economic conditions, and government policies. As of my last update, Malaysia had experienced periods of both low and moderate inflation in recent years.
Level of Corruption: Malaysia has taken steps to address corruption and improve governance. The country’s ranking on the Corruption Perceptions Index (CPI) has seen fluctuations over time. Efforts have been made to enhance transparency and accountability, and high-profile cases related to corruption have led to investigations and legal actions.
Currency Stability: The stability of a currency depends on factors such as economic conditions, government policies, global market trends, and geopolitical stability. As of my last update, the Malaysian Ringgit had experienced fluctuations in the past, including periods of depreciation and appreciation against other major currencies.
Economic Considerations: Malaysia has a diversified economy with sectors such as manufacturing, services, agriculture, and tourism contributing to its GDP. The country is known for being one of the “Asian Tigers” with rapid economic growth and industrialization in past decades.
- Export-Oriented Economy: Malaysia is a significant exporter of products like electronics, petroleum, palm oil, and rubber. Its trade relationships with countries such as China, Singapore, and the United States play a crucial role in its economy.
- Tourism: Malaysia’s natural beauty, cultural diversity, and modern infrastructure have contributed to its growth as a popular tourist destination.
- Investment: Malaysia has attracted foreign direct investment (FDI) due to its strategic location, skilled workforce, and business-friendly policies.
- Government Initiatives: The government has launched various initiatives to stimulate economic growth, including the development of economic corridors and infrastructure projects.
It’s important to note that economic conditions, currency stability, and corruption levels can change over time. For the most current and accurate information, it’s recommended to consult recent economic reports, financial news sources, and relevant government or international organizations’ publications.
If you’re considering financial matters related to Malaysia, such as investments or currency exchange, it’s advisable to consult financial advisors or experts with knowledge of the current economic situation and market trends.
Language and Culture
Malaysia is a diverse and multicultural country with a rich blend of languages and cultures due to its multi-ethnic population. The two main ethnic groups are Malays (Bumiputera) and Chinese, followed by Indians and various indigenous groups. This diversity is reflected in the languages spoken, religions practiced, and cultural traditions. Here’s an overview of the language and culture of Malaysia:

Languages:
- Bahasa Malaysia (Malay): Malay is the official language of Malaysia. It’s widely spoken and understood throughout the country. It’s used in government, education, and media.
- Chinese Languages: Mandarin, Cantonese, Hokkien, and other Chinese dialects are spoken by the Malaysian Chinese population. Mandarin is commonly taught in schools and is used in business.
- Tamil: Tamil is spoken by the Malaysian Indian community, particularly among the Tamil-speaking South Indian diaspora.
- Indigenous Languages: Malaysia is home to various indigenous groups, each with their own languages and dialects.
Culture:
- Religious Diversity: Malaysia is a multi-religious society. Islam is the official religion and holds a significant place in the culture. Buddhism, Christianity, Hinduism, and other faiths are also practiced. Religious festivals and holidays are widely celebrated.
- Festivals: Malaysia celebrates a variety of cultural festivals, including Hari Raya (Eid), Chinese New Year, Deepavali (Diwali), and Christmas. These celebrations are often marked by festive decorations, cultural performances, and traditional foods.
- Cuisine: Malaysian cuisine is renowned for its diversity and fusion of flavors. The cuisine reflects the country’s multicultural heritage, with influences from Malay, Chinese, Indian, and indigenous traditions. Popular dishes include nasi lemak, roti canai, satay, and rendang.
- Arts and Music: Traditional arts like wayang kulit (shadow puppetry), batik art, and various dance forms are an integral part of Malaysian culture. Modern Malaysian music often blends traditional elements with contemporary genres.
- Clothing: Traditional clothing includes the Baju Melayu for men and Baju Kurung for women, often worn during special occasions. Sarongs and kebayas are also popular. However, modern attire is commonly worn in daily life.
- Etiquette and Respect: Malaysians generally value respect and politeness. It’s customary to remove shoes when entering homes and some places of worship. When visiting someone’s home, it’s polite to bring a small gift.
- Greetings: Malaysians often greet each other with a handshake and a smile. Among close friends and family, hugs and cheek kisses might be exchanged.
- Language and Culture Preservation: While English is widely spoken, making communication relatively easy for tourists and expatriates, understanding basic local phrases can enhance cultural interactions.
Malaysia’s diverse language and culture contribute to its vibrant and unique identity. Embracing the different languages and cultural practices can lead to a richer and more immersive experience while living in or visiting Malaysia.
Social Support and Community
Social support and community in Malaysia are influenced by the country’s cultural diversity, traditions, and societal norms. Malaysians generally place importance on family ties, community connections, and mutual assistance. Here’s an overview of social support and community aspects in Malaysia:
Family Structure: Family is a cornerstone of Malaysian society, and strong family bonds are often emphasized. Many Malaysians live in extended family households, with several generations living together. Family members often provide emotional, financial, and caregiving support to one another.

Community Values: Malaysian culture places importance on community values, such as respect for elders, mutual assistance, and maintaining harmony within the community. These values are often reinforced through cultural practices and traditions.
Religious and Cultural Diversity: Malaysia’s multi-ethnic and multi-religious population contributes to a diverse social fabric. Communities often celebrate each other’s cultural and religious festivals, fostering a sense of unity.
Local Organizations and Associations: In many neighborhoods, you’ll find various community organizations, religious groups, and associations that provide support and organize activities. These groups often play a role in promoting social interaction and helping members in need.
Volunteerism and Charity: Volunteer work and charity are important aspects of Malaysian society. Many individuals and groups engage in volunteering and charitable activities to help those less fortunate. These efforts can range from distributing food to supporting education and healthcare initiatives.
Neighborly Support: In urban areas, neighborly support might vary, but in smaller towns and rural areas, neighbors often have close relationships and readily offer assistance when needed.
Online Communities and Social Media: With the rise of technology, online communities and social media platforms provide platforms for Malaysians to connect and interact. These digital communities can play a role in fostering connections, sharing information, and providing support.
Elderly Care: Respect for elders is a significant cultural value. Many families prioritize caring for elderly relatives at home, and there are also care facilities available for senior citizens.
Public Assistance Programs: Government programs and organizations provide support for vulnerable populations, including financial assistance, healthcare services, and education support. These programs are designed to help those in need, such as low-income families and individuals with disabilities.
Language and Cultural Barriers: While Malaysia’s diversity is a strength, language and cultural differences can sometimes create barriers to community integration, especially for expatriates or those from different cultural backgrounds.
Overall, Malaysia’s social support and community dynamics are influenced by a mix of cultural, religious, and societal factors. Engaging with local communities, participating in social events, and getting involved in volunteer work can help individuals feel a sense of belonging and connection within Malaysian society.
Legal System
Malaysia has a legal system that is a combination of several elements, including Islamic law (Sharia), English common law, and local customary law. The legal system is designed to accommodate the country’s diverse population and historical influences. Here’s an overview of the legal system in Malaysia:
1. Dual Legal System: Malaysia operates a dual legal system, with different laws applying to different segments of the population:
- Civil Law: Civil law principles are based on the English common law system. This system governs matters related to contracts, torts, property, family law, commercial law, and more. The civil law system is often referred to as the “civil jurisdiction” and is influenced by English law.
- Islamic Law (Sharia): Islamic law, or Sharia, is applied to Muslims in matters of personal status, such as marriage, divorce, inheritance, and religious affairs. Sharia is implemented through Sharia courts and is primarily based on the interpretation of Islamic principles.
2. Courts: Malaysia has a hierarchy of courts that handle different types of cases:
- Federal Court: The highest court in Malaysia, the Federal Court, deals with constitutional matters, civil and criminal appeals, and matters involving federal law.
- Court of Appeal: The Court of Appeal hears appeals from lower courts and is the second-highest court in Malaysia.
- High Court: High Courts are found in each state and federal territory. They have jurisdiction over civil and criminal matters and serve as courts of first instance for certain cases.
- Sharia Courts: Sharia courts handle matters related to Islamic law for Muslims. These courts are divided into two levels: the Syariah High Court and the Syariah Subordinate Courts.

3. Customary Law: Indigenous customary law is recognized in some areas, especially in matters related to land and native rights for indigenous communities in the states of Sabah and Sarawak.
4. Statutory Laws: Malaysia’s legal framework is shaped by statutes enacted by the federal and state legislatures. The Federal Constitution is the supreme law of the land and provides the foundation for the legal system.
5. Role of Precedent: The doctrine of judicial precedent is followed in Malaysia’s common law system. Decisions of higher courts serve as binding precedents for lower courts, providing consistency and predictability in legal decisions.
6. English Language: English is widely used in the legal system, and many legal documents and court proceedings are conducted in English.
7. Syariah Law and Civil Law Interaction: The interaction between the civil law system and Islamic law can sometimes lead to complex legal situations, especially in matters involving conversion between religions, jurisdiction disputes, and matters involving Muslims and non-Muslims.
Given the complexity of Malaysia’s legal system, seeking legal advice from qualified professionals, whether you’re a resident or an expatriate, is crucial when dealing with legal matters. Legal professionals can help navigate the intricacies of the system and ensure that your rights and obligations are understood and protected.
Climate and Environment
Malaysia’s climate and environment are characterized by tropical conditions, lush rainforests, diverse ecosystems, and a mix of coastal areas and highland regions. Here’s an overview of the climate and environment in Malaysia:
Climate: Malaysia has a tropical climate with high temperatures and humidity throughout the year. The country experiences two main monsoon seasons:
- Southwest Monsoon (May to September): During this period, the southwestern monsoon brings heavy rainfall to the western coast and central region of Peninsular Malaysia, including Kuala Lumpur. The eastern coast experiences drier conditions.
- Northeast Monsoon (November to March): The northeastern monsoon brings rain to the eastern coast of Peninsular Malaysia and the northern part of Borneo (Sabah and Sarawak).
Between these monsoon seasons, Malaysia generally experiences higher temperatures and more consistent weather conditions.
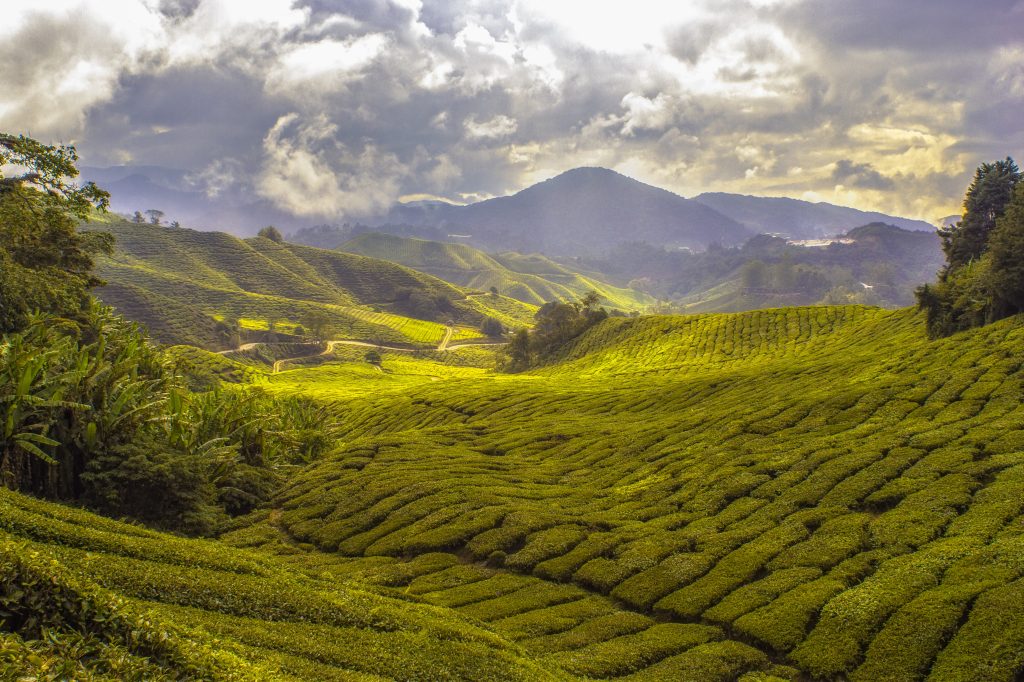

Environment: Malaysia is known for its diverse and lush environment, including rainforests, mangroves, coastal areas, mountains, and coral reefs. Here are some key features of Malaysia’s environment:
- Rainforests: Malaysia is home to some of the oldest rainforests in the world, including the famous Taman Negara National Park. These rainforests are rich in biodiversity and house a wide variety of plant and animal species.
- Biodiversity: Malaysia’s diverse ecosystems support a vast array of wildlife, including orangutans, tigers, elephants, and various bird species. The country’s biodiversity is both remarkable and fragile, with many species considered endangered.
- Coral Reefs: The coastal areas of Malaysia, particularly around islands like Langkawi and Tioman, feature beautiful coral reefs. These reefs are popular for diving and snorkeling, showcasing vibrant marine life.
- Mangroves: Mangrove forests thrive along Malaysia’s coastlines. These ecosystems provide critical protection against erosion and support a range of marine species.
- Highland Areas: Malaysia has highland regions with cooler temperatures, such as the Cameron Highlands. These areas are known for their tea plantations and scenic landscapes.
- Conservation Efforts: Malaysia is committed to preserving its natural heritage through various conservation efforts and national parks. However, issues such as deforestation and habitat loss pose challenges to maintaining this rich environment.
- Climate Change: Malaysia, like many other countries, faces challenges related to climate change, including rising sea levels, changes in rainfall patterns, and the potential impact on ecosystems and communities.
It’s important to be mindful of the environment and practice responsible tourism and living habits when in Malaysia. Respecting nature and adhering to guidelines for protected areas helps ensure the preservation of the country’s beautiful landscapes and unique biodiversity.
Infrastructure and Amenities
Transportation:
- Roads and Highways: Malaysia has an extensive network of well-maintained roads and highways, connecting major cities and towns. The highways are equipped with toll systems.
- Public Transportation: Major cities like Kuala Lumpur offer efficient public transportation options, including buses, commuter trains, and light rail systems. The Mass Rapid Transit (MRT) and LRT systems in Kuala Lumpur are well-known for their modernity and connectivity.
- Airports: Malaysia has several international airports, with Kuala Lumpur International Airport (KLIA) being the main hub. It’s well-connected to various destinations around the world.
- Ports: Malaysia’s strategic location has made it a key player in maritime trade. Ports like Port Klang and Penang Port serve as important logistics hubs.

Housing and Accommodation:
- Residential Areas: Urban areas offer a variety of housing options, from high-rise apartments to suburban houses. Malaysia My Second Home (MM2H) program allows foreigners to purchase property and retire in the country.
- Hotels and Resorts: Malaysia boasts a range of accommodation options, including luxury resorts, boutique hotels, and budget-friendly lodgings, especially in tourist destinations.
Healthcare:
- Hospitals: Malaysia has both public and private hospitals that provide medical services. Many private hospitals are equipped with modern facilities and skilled medical professionals.
- Medical Tourism: The country is a popular destination for medical tourism due to its high-quality healthcare facilities and affordable medical treatments.
Education:
- Schools and Universities: Malaysia has a variety of educational institutions, including international schools, public universities, and private colleges. English is widely used as a medium of instruction.
Utilities:
- Electricity and Water: Malaysia has reliable electricity and water supply. The voltage is 240V with a frequency of 50Hz.
Communication:
- Telecommunications: Telecommunication infrastructure is well-developed, with widespread mobile phone coverage and high-speed internet services available.
Entertainment and Amenities:
- Shopping Malls: Major cities have numerous modern shopping malls that offer a wide range of retail outlets, restaurants, entertainment centers, and cinemas.
- Cultural and Recreational Facilities: Malaysia has cultural centers, museums, art galleries, and recreational parks that showcase its rich heritage and provide leisure activities.
- Restaurants and Cuisine: Malaysia is known for its diverse and vibrant food scene, with restaurants offering local and international cuisines.
- Recreation: Outdoor activities such as hiking, water sports, and golfing are popular due to Malaysia’s diverse landscapes.
Overall, Malaysia’s infrastructure and amenities are designed to provide residents and visitors with a comfortable and modern lifestyle. It’s important to research specific regions to understand the available facilities and services in the area you plan to live or visit.
Political Stability and Safety
Malaysia has a multi-ethnic and multicultural society. It operates as a constitutional monarchy with a parliamentary democracy. The country has experienced relatively peaceful transitions of power through democratic elections. The political landscape is characterized by a variety of parties, and elections are held at regular intervals. There have been instances of political debate and disagreements, but the country has managed to maintain a stable governance structure.
Safety: Malaysia is generally considered safe for both residents and tourists. Violent crime rates are relatively low compared to many other countries. However, like in any country, it’s important to take common-sense precautions to ensure your safety:
- Crime: Petty theft and pickpocketing can occur, particularly in crowded areas and tourist hotspots. Be cautious of your belongings and avoid displaying valuable items openly.
- Health and Hygiene: Malaysia has good healthcare facilities, but it’s advisable to have health insurance to cover any medical expenses. Ensure you’re up to date on required vaccinations before traveling.
- Natural Disasters: Malaysia is located in a region prone to natural disasters such as floods, landslides, and occasional earthquakes. It’s a good idea to be aware of the local emergency procedures.
- Local Laws and Customs: Familiarize yourself with local laws and customs to avoid any unintentional breaches. Respect the local culture and traditions.
- Travel Advisories: Check travel advisories issued by your country’s government before traveling to Malaysia. These advisories provide up-to-date information on safety and security concerns.
- COVID-19: As of my last update, the COVID-19 pandemic had global implications, including in Malaysia. Travel restrictions and safety measures might be in place. Check the latest guidelines and restrictions related to COVID-19 before planning your trip.
Pension and Social Security
Here are some aspects of the pension and social security system in Malaysia:

Employees Provident Fund (EPF): The Employees Provident Fund is a mandatory savings program for private-sector employees. Both employees and employers contribute a portion of the employee’s salary to the EPF. This fund acts as a retirement savings scheme, and individuals can withdraw their EPF savings upon reaching a certain age or meeting specific conditions.
Civil Service Pension Scheme: Government employees and civil servants are typically covered under a pension scheme provided by the government. This scheme offers retirement benefits to eligible government employees based on their years of service and salary.
SOCSO (Social Security Organization): SOCSO provides social security protection to employees in the event of work-related injuries, disabilities, or death. It offers financial assistance, medical care, and rehabilitation services to eligible workers and their dependents.
Public Assistance Programs: Malaysia has various public assistance programs that provide financial aid to low-income individuals and households. These programs are administered at the state level and aim to support those in need.
Retirement Planning: Since Malaysia lacks a comprehensive national pension system, individuals are encouraged to plan for their retirement through personal savings, investments, and other financial instruments. Many people rely on their EPF savings and private savings to support themselves during retirement.
It’s important to note that social security and pension systems can vary for different groups of people, such as private-sector employees, government employees, and self-employed individuals. For individuals planning to retire in Malaysia, it’s recommended to understand the specific retirement and social security options available to them based on their employment status and circumstances.
Given the complexity of retirement planning and financial considerations, consulting with financial advisors or experts who are familiar with Malaysia’s regulations and options can provide valuable guidance tailored to individual needs and goals.
Adapting to Change
Adapting to living in Malaysia as a person from a Western country can be a rewarding experience, but it also comes with its own set of challenges. The ease of adaptation can vary based on factors such as cultural differences, lifestyle preferences, personal mindset, and the location within Malaysia. Here are some points to consider:

Positives:
- Cultural Diversity: Malaysia’s cultural diversity can make it a welcoming and enriching environment for people from Western countries. The country’s mix of traditions, languages, and customs can lead to unique cultural experiences.
- Language: English is widely spoken in Malaysia, making communication and daily life easier for expatriates. Most signs, official documents, and services are available in English.
- Cost of Living: Malaysia’s cost of living can be lower than that of many Western countries. This can provide expatriates with the opportunity to enjoy a comfortable lifestyle at a relatively affordable cost.
- Food: Malaysia is renowned for its delicious and diverse cuisine. Expatriates often appreciate the availability of both local dishes and international options.
- Modern Infrastructure: Major cities like Kuala Lumpur offer modern infrastructure, including transportation, shopping centers, medical facilities, and entertainment options.
Challenges:
- Cultural Adjustment: While Malaysia’s cultural diversity is a positive aspect, it can also require adjustment for expatriates who are not accustomed to the customs, social norms, and religious practices.
- Weather and Climate: Malaysia has a tropical climate with high humidity and temperatures. The heat and humidity might take some time to get used to, particularly for those coming from cooler climates.
- Bureaucracy: Navigating administrative processes, visa applications, and other bureaucratic aspects can sometimes be challenging for expatriates.
- Language Variations: While English is widely spoken, accents and local terms might vary, leading to occasional communication misunderstandings.
- Healthcare Considerations: While healthcare in Malaysia is generally good, expatriates should ensure they have adequate health insurance coverage to manage medical expenses.
- Cultural Sensitivity: Being aware of cultural norms and practices is important to avoid unintentionally offending or disrespecting local customs.
- Different Work Culture: If you’re moving for work, adapting to the local work culture might take some time. Malaysians often place emphasis on building personal relationships and showing respect in professional settings.
Adapting to life in Malaysia as an expatriate involves an open mindset, a willingness to embrace new experiences, and an understanding that there will be both positive and challenging aspects. Engaging with the local community, seeking cultural insights, and learning about Malaysia’s history can enhance your adaptation process. It’s recommended to connect with expatriate communities, seek advice from those who have already lived in Malaysia, and approach the experience with curiosity and a positive attitude.
